Industrial Brush
Brushes are used in various applications in the industrial world.
To date, we have used a wide variety of products (cleaning, cleaning, conveyance, polishing, affixing, destatic, etc.)
We responded to the requests of factories, machine manufacturers, research institutes, etc., and manufactured them.
If you are considering something new or have trouble with an existing product, please contact us.
◎We will propose the optimal production method considering the selection and usage of the optimal hair material according to the application.
If you are considering it, please contact the following.
- Contact: Uno Hake Brush manufacturing Co.,Ltd
- TEL:+81-33622 9078
- FAX:+81-33622-7049
- e-mail:unobrush@extra.ocn.ne.jp
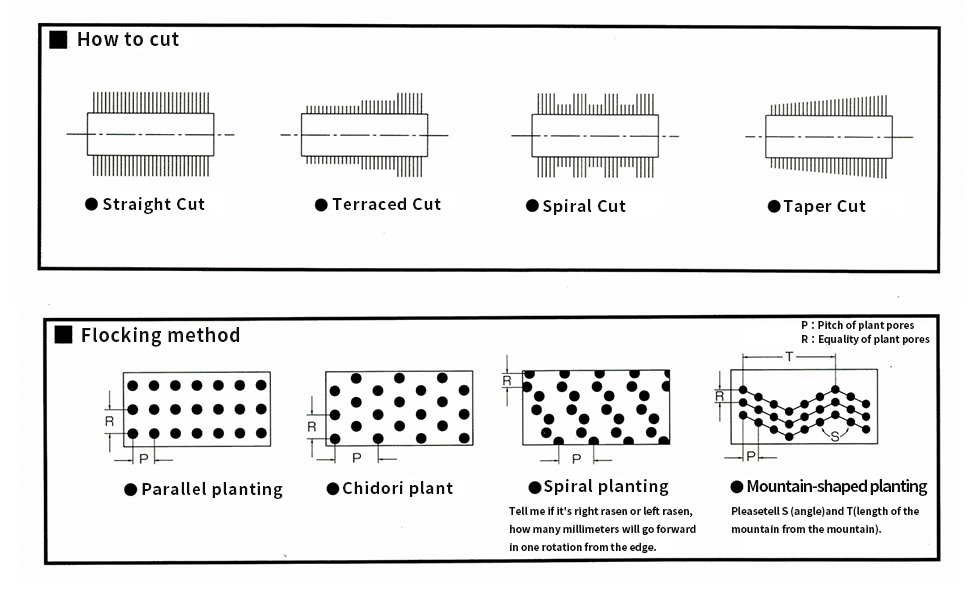
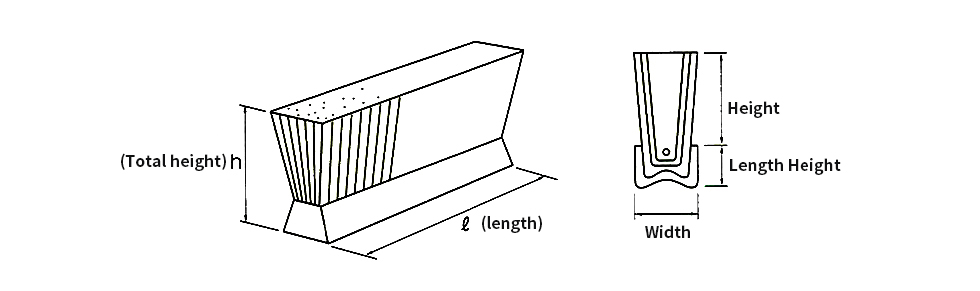
Board brush
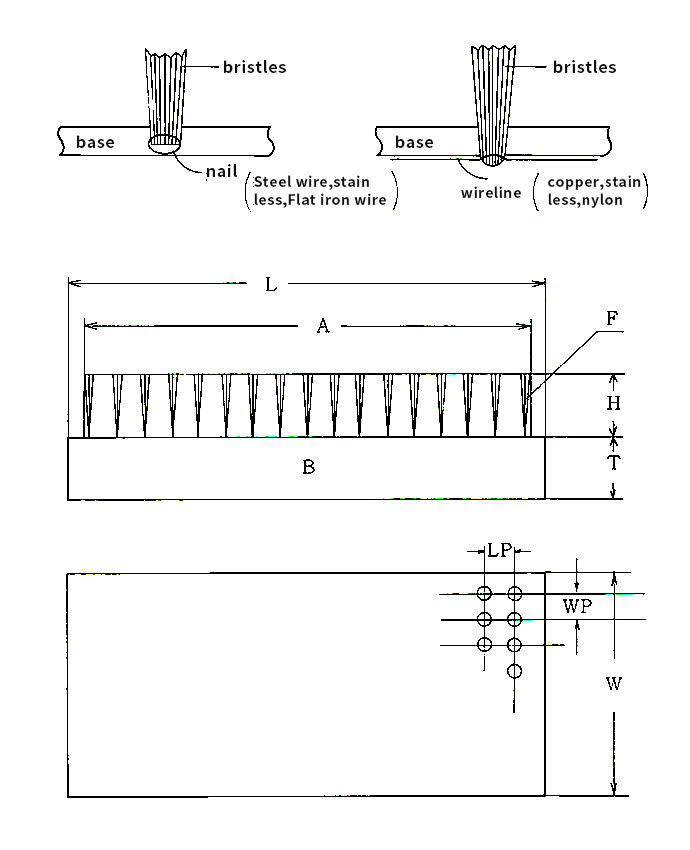
- L: Wood (brush stand) total length
- A: Brush effective width (wading)
- F : Brush hair(hair): Chemical fiber, animal fiber, plant fiber, metal wire
- B:brush stand, wood(beech, rawan, wig,sakuraetc) metal, synthetic resin
- H: hair length
- T: Brush stand thickness
- LP : brush pitch (L directionpitch)
- WP :(W directionpitch ) (displayed in normal row number)
- W:Number of holes determined by brush stand width LP / WP
Disk Brush
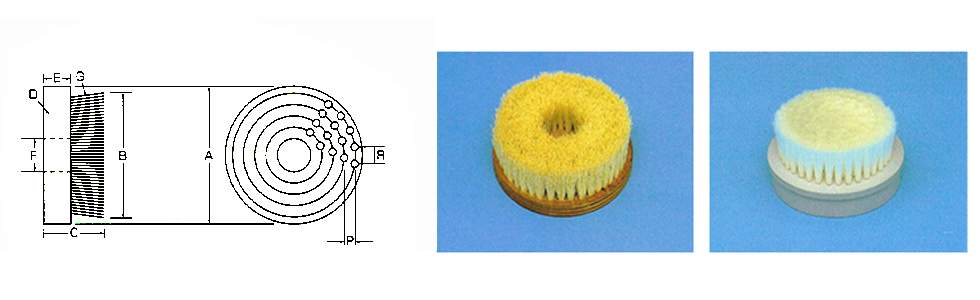
- A- Outer diameter of flocking table
- B- Flocking width
- C- Total height
- D- Material of flocking table
- E- Thickness of flocking table
- F- Inner diameter of flocking table
- G-brush wire rods
- P- Pitch of plant pores
- R - Equality of plant pores
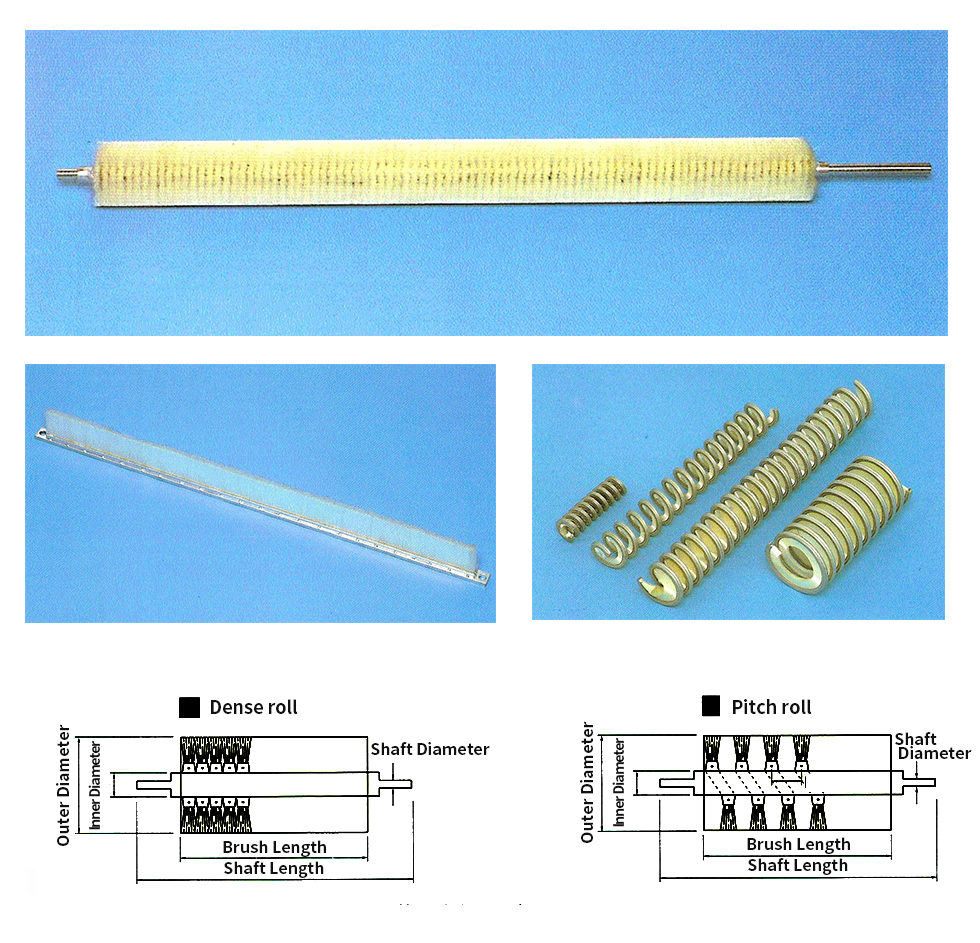
Roll brush
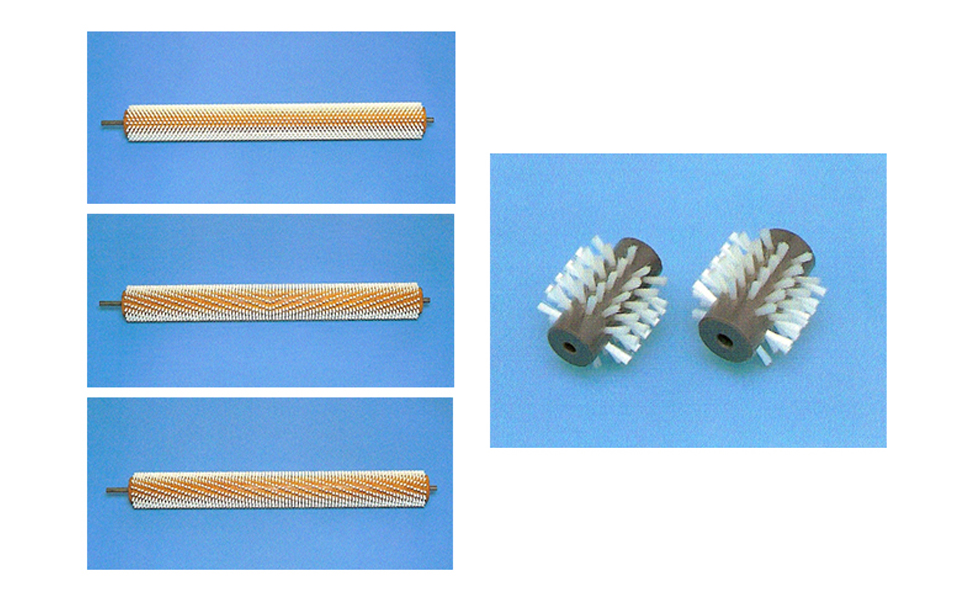
Roll brush illustration
Mechanical flocking
- Roll wood (base)
- Lumber (wig, rawan, beech, etc.) synthetic resin
- Brush (hair quality)
- metal wire (hard steel wire, iron wire, sten wire, middle wire, etc.)
- Chemical fibers (nylon, PVC fiber, P. P Tregred, etc.)
- Animal fibers (main hair, furi, bella, pig hair, etc.)
- Plant fibers (paquine, fern, throg, etc.)
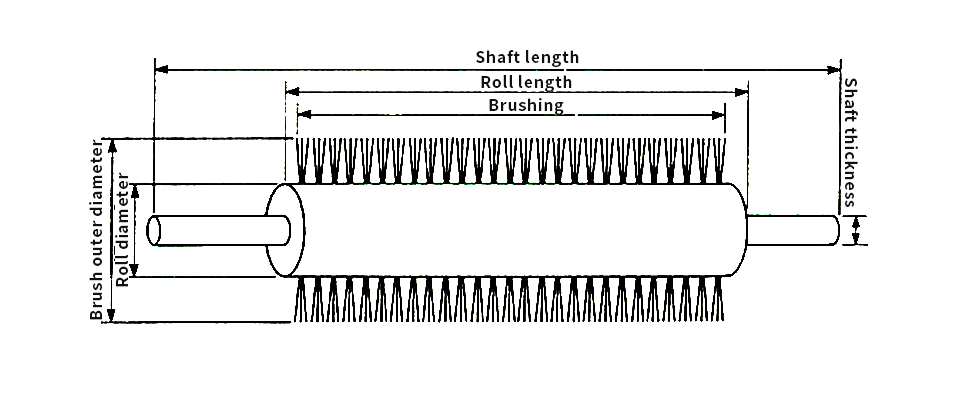
Split Roll Brush
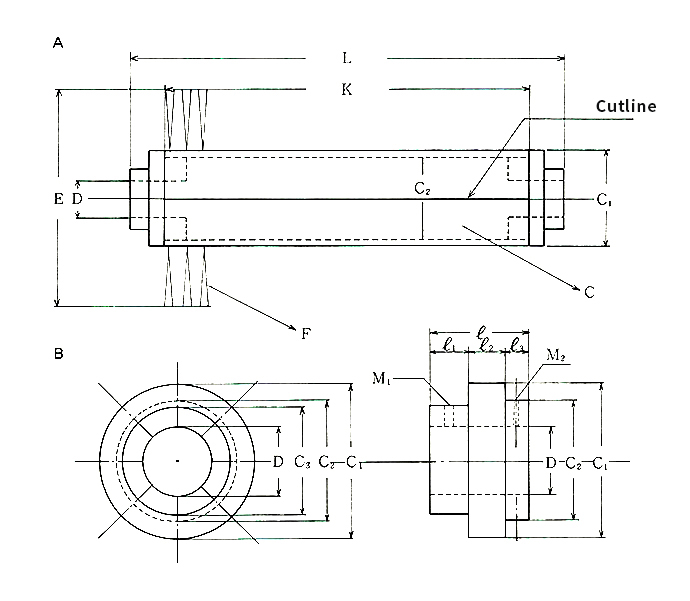
Split rolls can be manufactured for both hand
flocking and machine flocking.
- A: Roll Brush
- B: Flange
- C : Roll(Wood)Timber, Synthetic Resin, Iron, Aluminum
- D: Shaft Diameter
- E: Roll Brush Outer Diameter
- F:Brush (Hairy) Chemical Fiber, Animal Fiber, Plant Fiber, Metal Wire
- K: Brush Effective Width (Wasting)
- L: Roll Brush Total Length (Flange Included)
- C1 : Roll Wood Outer Diameter (Flange Outer Diameter)
- C2 : Roll Wood Inner Diameter
- C3: Flange Protrusion L: Flange Total Length
- L1: Flange Protrusion
- L3: Roll Wood Fixed Protrusion
- M1: Shaft Fixing Screw Hole
- M2: Roll Wood Ground Fixing Screw Hole
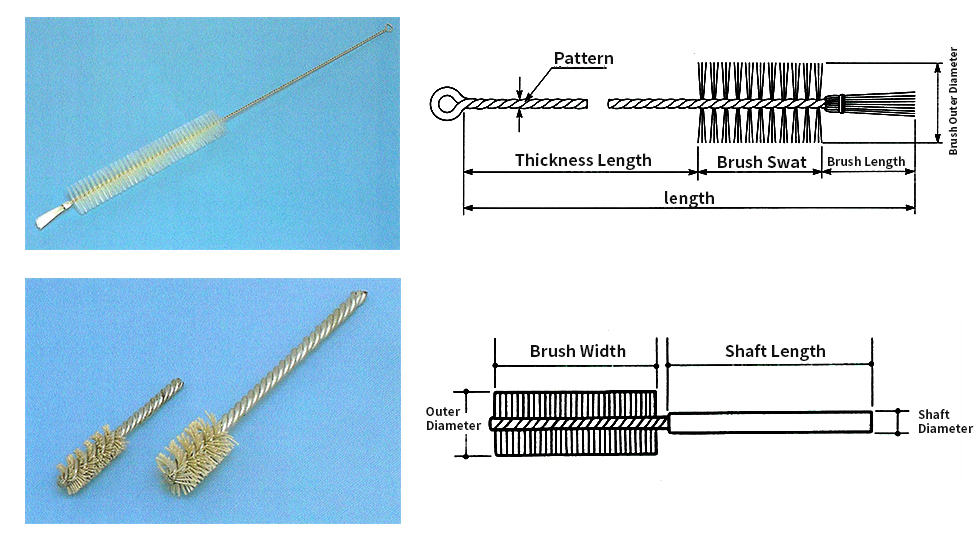
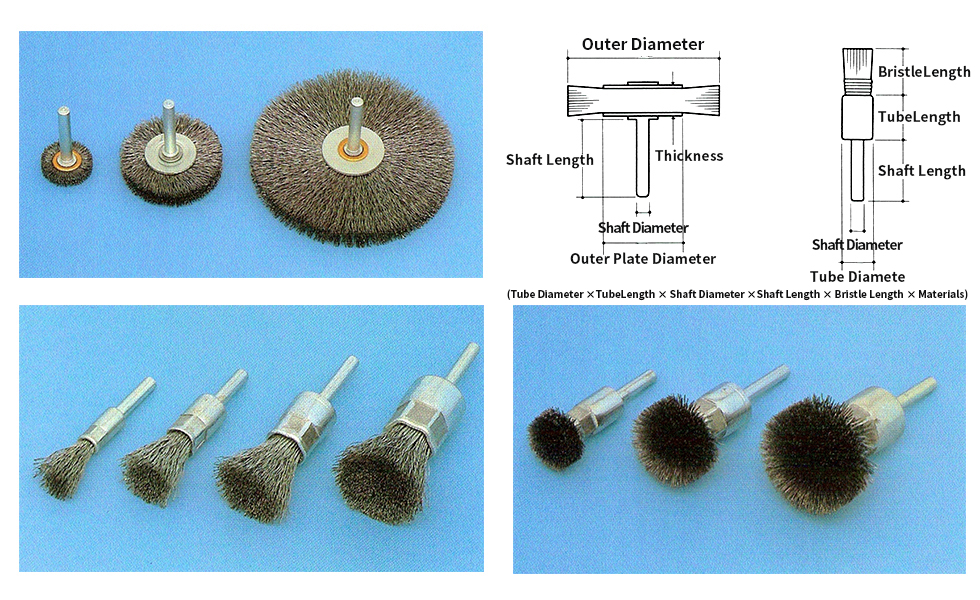
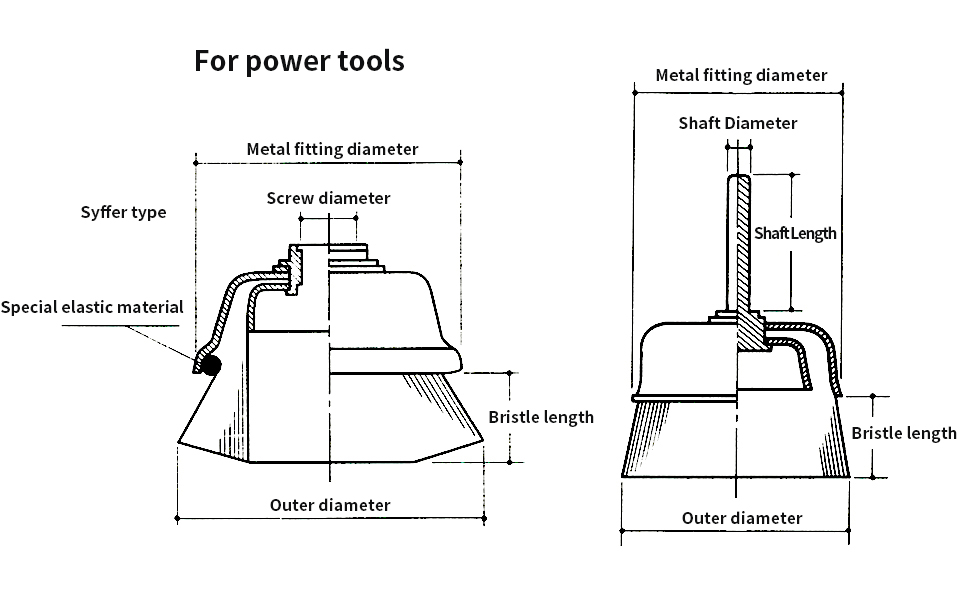
Screw brush
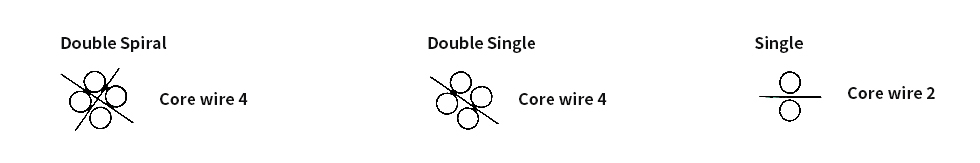
- ・ There are three types of screw brush shapes: double spiral, double single, and single.
Channel Brush
- ・The roll brush is securely fixed to the shaft, coor, etc., so it does not deform.
- ・The outer diameter can beproduced from φ30toφ1,000, andthe brush length can be produced up toabout 4,500mm.
Channel standard table
| Channel type | wide | high | Minimum inner diameter |
Channel material | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No.3Channel | 3 | 4 | 6 | Galvanized soft steel sheet |
stainless |
| No.5Channel | 5 | 6 | 10 | 〃 | 〃 |
| No.6Channel | 6 | 7 | 15 | 〃 | 〃 |
| No.8Channel | 8 | 9 | 38 | 〃 | 〃 |
| No.10Channel | 10 | 11 | 90 | 〃 | 〃 |
| No.13Channel | 13 | 14 | 160 | 〃 | 〃 |
Examples of mounting brackets
Wheel Brush
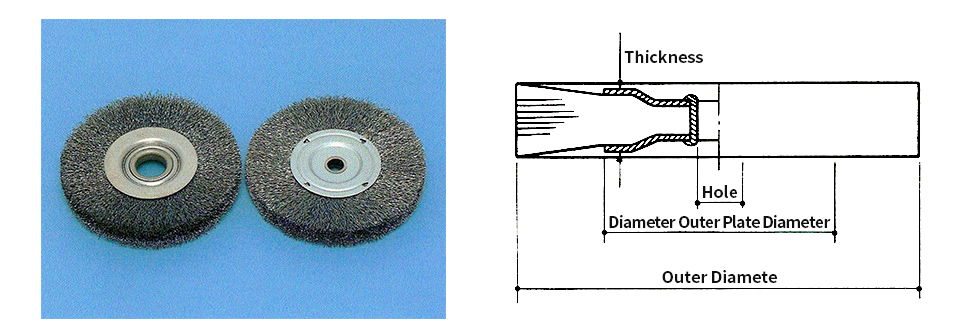
Wheel brush with axis

Wheel Brush
Hair materials used in brushes and brushes
| Animal fiber | Hair-made animal hair. Horse hair, pig hair, mountain wool, deer hair, man's hair, boar hair, tanuki hair, weatin hair |
|---|---|
| Plant fiber | We make hair from the epidermis, leaves, roots, and other fibers of plants. Paquin Palm Fern Suro Karkaya Sisal Bron Thang |
| Chemical fiber | fibers by chemical synthesis. Nylon, grit nylon, polypropylene, vinyl chloride, polyester, aramid fiber, fluorine fiber, antistatic fiber |
| Metallic | Steel wire, stainless steel wire, brass wire, phosphor bronze, piano wire, plating wire, twist wire, wrapping, needle wire |
Wood, resin, and metal used in brushes and brushes
Beech, cherry tree, green tree, katsura, sen, autumnal leaves, rowan, bamboo, coctan, cedar, ho, pine, tochi, paulownia, veneer
Materials for brushes and brushes [animal fibers]
| Name | Characteristics and physical properties | use |
|---|---|---|
| use |
Chemical resistance is somewhat better than chemical fiber. Because it is a natural material, there is a limit in length, and the thickness is not constant. Flexible, resilient and static less likely to occur. |
・ For polishing, painting, cleaning, payment, etc. |
| Guinea pig hair |
Because it is a natural material, there is a limit in length, and the thickness is not constant. It is flexible, resilient and has a strong waist. Ideal for brush and brush hair materials. |
・ For polishing, painting, cleaning, payment, etc. |
| Mountain wool |
Because it is a natural material, there is a limit in length, and the thickness is not constant. The waist is softer than horse hair and pig hair, and the area is soft. |
Brushes, brushes, brushing, glazing, etc. |
| Deer hair |
It is flexible and soft, but easy to cut. Because it is a natural material, there is a limit in length, and the thickness is not constant. |
・ For dyeing, painting, painting, and others |
| Human hair |
It is flexible and soft. Because it is a natural material, there is a limit in length, and the thickness is not constant. |
・Lacquer brush, oil brush, painting, etc. |
Materials for brushes and brushes [plant fibers]
| Name | Characteristics and physical properties | use |
|---|---|---|
| Paquin (Tampico) |
It is a fiber from the leaves of Tampico hemp native to Mexico, which is relatively hard, has high water absorption, and is suitable for cleaning and polishing. It also has high heat resistance (about 80 degrees). White and black (dye). |
・ For various cleaning, woodworking products glazing, precious metals, jewelry polishing, general industrial buffing |
| palm |
It is a fiber of palm fruit, has high hydro content and excellent polishing cleaning power. Resilient and flexible. Decoroded white palm is similar to paquin. Native to Sri Lanka. |
Twasi, Hawki, Mat, Car Wash Brush |
| palmyra stalk |
High hydro content in fibers taken from palm leaves, Because it is hard, it is suitable for cleaning and cleaning. |
Polisher, deck brush, hawk |
| hemp palm |
Among plant fibers, it is the most corrosion resistant and elastic. The fiber is hard and short. Wear is low. |
Matt.Hoki Twasi |
| Kalkaya | It is a fiber taken from the root of Memarkaya and bristles. |
Brush for uzkuri, tawasi, livestock, and polishing |
| sisal | It is a fiber taken from hemp and has excellent polishing power. | Buff.body brush |
| Bron |
Palmyra palm leaves are scraped off, hard and elastic with fiber only on the back axis. |
Load sweeper |
| tsugu |
It resembles a fern, but it is hard, has a heavy specific gravity, and has a black color. |
Hoki |
Brush Material [Chemical Fiber]
| name | Characteristics and physical properties | specific gravity |
Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| nylon 6 types , 66 types 610 Type / 612 Type 〔Toray〕 [DuPont Thainex] 〔Azron〕 〔Artron〕 |
Nylon fiber is abrasion resistant, strong, flexible, Excellent durability. <Melting point><Usage limits> 6 types 214°C 100°C Type 66 250°C 120°C Type 610 212°C 100°C Type 612 212°C 100°C |
1.14 1.14 1.14 1.14 |
φ0.1~φ1.6 φ0.1~φ1.5 φ0.063~φ1.0 φ0.063~φ1.0 |
| Grit Nylon (Nylon with abrasive material) Tregrid Tynex A SanGritte |
It is a material made by kneading abrasive materials (alumina oxide and silicon carbide) into nylon materials and processing them as monofilaments, and has excellent polishing power. |
2.56 | φ0.4~φ1.6 |
|
polypropylene (P.P) |
Harder than nylon material and stronger waist. While excellent in flexion resilience and elasticity, it is somewhat inferior to abrasion resistance, etc. <Melting point>170°C <Usage limits>80°C |
0.91 | φ0.1~φ2.5 |
| Vinyl chloride (P.V.C.) |
Harder than nylon material and stronger waist. <Melting point>135°C <Usage limits>60°C |
1.39 | φ0.1~φ1.6 |
| polyester (PET) (PBT) |
It is harder than PP and has the same specific gravity as PVC. |
1.38 | φ0.3~φ0.6 |
| Aramid fiber Cornex |
It is an ultra-heat-resistant fiber and has excellent abrasion resistance. |
1.34 | φ0.15~φ0.55 |
| Fluorine fiber (Teflon) (Toyoflon) |
Non-flaming, non-toxic, abrasion resistant and non-sticky. |
||
| Antistatic fiber Monofilament (Ernon) |
Uniform eronon emulsion on nylon With specially coated fibers, It is effective for electrostatic removal. |
φ0.2~φ0.3 | |
| Antistatic fiber Monofilament (Toyostat) |
Based on PVC material, conductive materials and metal particles are kneaded, It is effective for electrostatic removal. |
φ0.06~φ0.3 | |
| Antistatic fiber Multifilament (Thunderlon) |
Copper sulfide was bonded to acrylic and nylon materials. Organic conductive fiber is effective for electrostatic removal. |
15.6μ~40μ |
Brush Material [Metal Wire]
| name | Characteristics and physical properties | Diameter (mm) |
use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Copper wire (SW) |
By cold stretching, hardness is put out. It is used for general industrial brushes. It is relatively prone to rust and vulnerable to metal fatigue. In Japan, it is displayed by carbon content, Overseas, it may be displayed in intensity. 40℃~80℃ |
φ0.15~φ0.8 |
Rust removal peeling Deserring Scale removal Polishing and grinding Others |
|
Stainless steel wire (SUS) 〔304〕 〔316〕 |
It is resistant to chemicals in general and heat-resistant. It is more rust resistant and less damaged than SW lines. [304] may be magnetized in the work process, [316] does not magnetate. |
φ0.05~φ0.8 |
For polishing metal products such as stainless steel and aluminum Polishing work in chemicals, solutions and at high temperatures |
|
Brass wire (BSW) |
It is more flexible than SW line and SUS line. | φ0.06~φ0.8 |
Polishing, rust removal and de-desering of brass and copper products |
|
Phosphor bronze (PBW) |
With copper as the main ingredient, attach 3 to 9% tin, A 3-way alloy de-acidated with phosphorus. Corrosion resistant, abrasion resistant, elastic. |
φ0.06~φ0.6 |
Precision parts polishing Polishing of precious metals and jewelry |
| Piano wire |
Similar to SW line, The carbon content is 80C or more. |
φ0.15~φ0.8 |
Same as Copper wire(SW) |
| Plated wire |
It is plated with SW wire to improve corrosion resistance and strength. |
φ0.2~φ0.5 |
Cup, bevel Manual brush |
| Stranded wire |
A process in which multiple metal wire is twisted. |
φ0.25~φ0.38 |
Cup, bevel Manual brush |
| wrapping | A few plated lines bundled together. | φ0.25~φ0.38 |
Cup, bevel Manual brush |
Characteristics of chemical fibers
Characteristics of Nylon Bristle
Compared to various materials for brushes, the general properties of nylon bristles are as follows:
- ○ Wear resistance
- Nylon is one of the most abrasion-resistant natural and synthetic fibers and can withstand long-term use.
- ○ Elasticity and resilience
- It has moderate rigidity and elasticity, and has resilience to deformation.
- ○ Chemical resistance
- In general, it is a little weak against strong acids, but it is less likely to be affected by other alkali-containing chemicals, and is also durable for gasoline, oil, detergents, etc.
- ○ Heat resistance
- Can withstand moderate heat. However, there are some differences depending on the type of nylon.
- ○Sanitary
- It is hygienic because it does not contain harmful ingredients and does not rot.
- ○ Easy to handle
- Because the specific gravity is light, it is easy to handle processed products, and if it gets dirty, it is easy to remove dirt by simple washing with water, and it dries quickly because it has little moisture absorption.
Properties of Nylon Bristle
General properties
- ○ Nylon 6 (120T, 125T) has high pulling strength, but the bending hardness (rigidity) and dimensional change due to moisture absorption are changing more than other nylons.
- ○ Nylon 6.6 (305T, 315T) has excellent heat resistance.
- ○ Nylon 6.10 (200T, 205T) has a light specific gravity (1.08) and a very small water absorption rate, so the bending hardness (rigidity) and dimensional change due to water absorption are the smallest.
Table-1 Properties of Nylon Bristles
| type performance |
120T | 200T | 300T | Other resin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NY6 | NY6.10 | NY6.6 | P.B.T. | P.E.T | P.P | |
| rigidity | Soft | hard | Soft | hard | hard | hard |
| Pulling strength | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Restorability | ○ | ◎ | ○ | ◎ | ○ | △ |
| Abrasion resistance | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | ○ | △ |
| Heat resistance | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ○ | ◎ | △ |
| Weather resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | △ |
| Chemical resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
|
Dimensions by water absorption Change in bending hardness |
○ | ◎ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ |
※ (◎ Especially excellent ○ Excellent △ somewhat inferior)
General properties of nylon brissle
| type performance |
120T (NY6) |
200T (NY6・10) |
305T (NY6・6) |
Animal hair (pig hair) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The point of melting(℃) | 180 | 180 | 230~235 | - | |
| melting point(℃) | 214~220 | 212~214 | 250~260 | - | |
| specific gravity | 1.13~1.14 | 1.08~1.09 | 1.13~1.14 | 1.32~1.34 | |
| specific gravity | 18(standard state) 20℃-65%RH |
4.0~4.5 | 1.4~1.8 | 4.0~4.5 | 11.0~13.0 |
| 20℃-100% | 9.0~1.0.0 | 2.2~2.8 | 8.0~9.0 | - | |
| Dry tension strength (g/d) | 5.0~7.0 | 4.5~6.0 | 4.0~5.5 | 1.0~3.0 | |
| Dry stretch elongation (%) | 20~35 | 20~35 | 20~35 | 20~40 | |
| Boiling water shrinkage (%) | 3~10 | 1~4 | 1~4 | - | |
| Dry tension resistance (g/d) | 17~22 | 39~45 | 20~25 | - | |
| Young's Rate (Dry) (kg/㎟) | 180~230 | 380~440 | 210~260 | - | |
- ※ The number of tension strength and boiling water shrinkage rate varies slightly depending on the variety and thickness.
- ※ Because the animal hair is tapered shape, there is a difference in the number at the measurement position.
- ※ This figure was calculated using our measurement method. (Toray)
Chemical resistance
| chemical | performance | chemical | performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sulphuric acid | × | acetic acid | × | |
| nitric acid | × | Acetic aneric acid | × | |
| hydrochloric acid | × | Sodium acetate | ◎ | |
| hydrogen fluoride | × | formic acid | × | |
| chlorine | ◎ | Maleic anate | - | |
| hydrogen sulphide | ◎ | citric acid | △ | |
| Sulfur dioxide | ○ | fatty acid | ◎ | |
| Hiic acid | ○ | Phthalate anhunic acid | - | |
| boric acid | △ | hydrocarbon | ◎ | |
| Phosphate | △- | alcohol |
○(There's going to be an intrusion.) |
|
| potassium hydroxide | ○ | Isopropyl alcohol | ○(Dimensional changes occur) |
|
| sodium hydroxide | ○ | Pthyl Alcohol | ◎ | |
| ammonia | ○ | Glycerin | ○(trespass) | |
| Ane-water ammonia | ○ | glycol | ○(trespass) | |
| calcium hydroxide | × | ester | ◎ | |
| water | ◎(Dimensional change occurs) |
Ethyl acetate | ◎ | |
| sodium chloride | ◎ | Ethyl chloride | ◎ | |
| ammonium nitrate | ○ | ketone | ◎ | |
| sodium nitrate | ◎ | acetaldehyde | ◎ | |
| calcium carbonate | ◎ | urea | - | |
| Magnesium carbonate | ◎ | detergent | ◎ | |
| calcium chloride | ◎ | Tar oil | ◎ | |
| Magnesium chloride | ◎ | rosin | ◎ | |
| Magnesium nitrate | ◎ | Chlorinated solvents | ◎ | |
| Magnesium sulfate | ◎ |
Weight change ◎Excellent 2% or less 〇 Good +2-14%, -2--3% △Yes +14-19%, -3--4% bad |
||
| Zinc sulfate | ◎ | |||
| Zinc chloride | Dissolution at high temperatures |
|||
| Sodium hydrogen sulfate |
Total concentration, limit temperature*:◎ |
|||
| hydrogen peroxide | △ | |||
| Chromic acid | × | |||
| Electric Potash Chromic Acid | × | |||
(Ito: Plastic Data Handbook, Industrial Research Committee, 1980)
- (1) Dissolve in acids (concentrated liquid) and phenols.
- (2) It has little effect on water, soap, synthetic detergents, and dry cleaning solvents.










